What are the basics of NLP? What are the specific NLP capabilities that can be achieved with Watson NLP Library for Embed? Find out more in this blog.
In a recent blog posts I explained the capability to deploy NLP tasks as containers, focusing on how to deploy to various container runtimes Since then I’ve learnt a lot about the basics of NLP, the specific capabilities of Watson NLP for Embed, and how to find and run samples from IBM.
NLP Basics
NLP is a field which combines maths, linguistics and computer science. The goal is to get computers to do useful things with natural language data, for example classification, translation, summarization or assisted writing. Approaches to NLP have evolved over the decades, from simple rules to machine learning to deep learning/neural networks or even the latest transformer (aka large language) models.
For some NLP tasks, it may be sufficient to use a pre-trained model. For increased accuracy, algorithms can often be trained with domain specific data, which usually requires some data preparation.
Watson NLP Basics
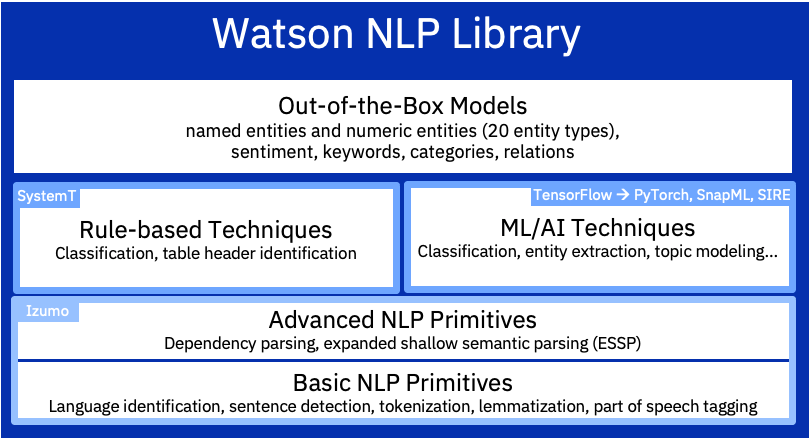
Watson NLP Library for Embed has an capabilities for all these tasks. It has primitives to help with data preparation, pre-trained models, and algorithms which can be custom trained.
For pre-trained models, IBM has taken special care about the data to train the models. This includes the quality of the data, the data provenance, and its intellectual property. This means that unlike some models in open-source NLP frameworks, you can can use IBM pre-trained models without worrying about license or intellectual property infringements.
For both pre-trained models and algorithms that must be trained with custom data, there may be a choice based on the four major NLP approaches:
- Rule-based - no training data required, very accurate, fast runtime inference
- Classic statistical ML algorithms - medium quality, fast runtime inference
- Deep-learning algorithms - high quality but data hungry, medium runtime inference
- Transformer-based algorithms - highest quality, slowest runtime inference
I won’t go into detail, but the approaches above include algorithms such as SVM, CNN, BilSTM and BERT.
NLP Primitives
These are powered by IBM’s Izumo which addresses common NLP tasks:
- Language identification - Support for 69 languages
- Sentence detection & Tokenization - Often the first step in NLP processing is to take a document and split it into words, sentences and tokens (words, numbers and punctuation).
- Lemmatization - Reduce a given word to its root word, taking into account that many similar words have essentially the same meaning.
- Part of Speech Tagging - Takes raw text and returns annotations (POS tags) such as noun, verb, adjective, plural noun, past-tense verb etc.
- Dependency Parsing - Determine the relationships between phrases in the sentence.
- Expanded Shallow Speech Parsing - Finding the set of grammar rules and their sequence that generated a sentence.
Rule-based Techniques
System-T is short for System Text, also known as RBR (rule-based runtime). It provides a query language which can be used to configure a rule based model to extract target mentions from text. For example, using a text corpus about nature, you might define a label ‘ANIMAL’ with keywords ‘cat’ and ‘dog’. The extraction algorithm has many operators to build complex rules. For example, dictionaries enable matching based on lemmas, so if you set a keyword ‘mouse’, the algorithm would also match for ‘mice’.
Machine Learning/AI Techniques & Pre-Trained ‘out-of-the-box’ NLP Models
The capabilities of Watson NLP are summarised below. Some capabilities can be achieved with a pre-trained model, others require training an algorithm with custom data (for classic ML or Deep Learning) or fine tuning (for transformer models).
When using custom training, most machine learning algorithms can’t take in raw text. Instead, you must perform “feature extraction” to convert raw text into numeric values and there are different ways to achieve this. Watson NLP provides popular approaches like GloVE, Universal Syntax Embeddings (USE) and BERT embeddings.
Sentiment & Emotion classification
- Sentiment classification refers to analyzing text for positive, neutral or negative sentiment.
Analysis is done at either document, sentence or for a targeted aspect. For document level, the sentiment score for individual sentences is aggregated. For aspect oriented, this focusses on sentences which contain a specified span of text.
- Pre-trained model(s) available: Yes
- Can be custom trained: Yes
Entities Phrase extraction
- Entities can include names of people, organization names, dates, prices, and facilities. Entities can be pre-trained or added for custom scenarios.
Entities can be extracted from text.
- Pre-trained model(s) available: Yes
- Can be custom trained: Yes
Keywords & Phrase extraction
- Phrases are non-overlapping noun phrases from the input text. A noun phrase is small group of words which contains a noun but doesn’t contain a verb
Keywords from a document can accurately describe the document’s content and can facilitate fast information processing. They are created using the output of Phrases and ranked according to how important they are in the document.
- Pre-trained model(s) available: Yes
- Can be custom trained: No
Topic Modeling
- Extract topics from data, for example complaint data from banking customers.
- For example, customer service teams can sort the data to understand what the main problems are and route them to the right experts.
Topic modeling does not require that the topics are pre-defined, the main themes are identified by analyzing the text.
- Pre-trained model(s) available: No
- Can be custom trained: Yes
Text Classification
Classify a data set into multiple pre-defined classes, e.g. customer reviews of hotels are classified in ‘non-complaint’ and ‘complaint’
- Pre-trained model(s) available: No
- Can be custom trained: Yes
Text Categorization
- Organize a dataset into a hierarchical categorization system, for example categorize news articles into a topology like politics, sports, entertainment.
If the dataset already has a broad category labels, text categorization could be used to define more fine grained categories. For example, politics is further categorized into foreign policy, education, health etc
- Pre-trained model(s) available: Yes
- Can be custom trained: Yes
Relation Extraction
Extract relations between two entity mentions. For example, in the text “John Smith drives for Uber.”, the entities John Smith and Uber are in a relationship with each other, and the relationship type is ‘works for’.
- Pre-trained model(s) available: Yes
- Can be custom trained: Yes
Co-reference Resolution
Grouping multiple entity mentions in the input text that refer to the same real-world entity. For example, in the text ‘Anna Smith is an engineer. Anna loves her job at IBM.’, ‘Anna Smith’ and ‘Anna’ refer to the same entity.
- Pre-trained model(s) available: Yes
- Can be custom trained: Yes
Concept Extraction
Extract general DBPedia concepts that are directly referenced or alluded to (but not directly referenced) in the input text. For example, in the text ‘IBM announces new advances in quantum computing’, a concept extracted may be http://dbpedia.org/resource/IBM, http://dbpedia.org/resource/Quantum_computing and http://dbpedia.org/resource/Qubit.
- Pre-trained model(s) available: Yes
- Can be custom trained: No
Topical Clustering
- Performs a topical clustering analysis over a collection of documents.
Documents are clustered into different groups based on a similarity measure.
- Pre-trained model(s) available: No
- Can be custom trained: Yes
PII Entities
- The PII models recognize personal identifiable information such as person names, SSN, bank account numbers, credit card numbers, etc.
- The majority of types rely on looking for common formats and performing checksum/validations, e.g. to validate a credit card number.
Other entities like persons and locations use a pre-trained model.
- Pre-trained model(s) available: Yes
- Can be custom trained: No
Samples
Samples which demonstrate both pre-trained models, and training ML/AI algorithms can be found here
Development Environment
The Watson NLP libraries are available in processing environments for Watson Studio (which includes Jupyter Notebooks). Watson Studio is available via IBM Cloud Pak for Data as a Service on IBM Cloud, or on-premises. A free trial is available.
Putting it all Together
When you’re ready to deploy a pre-trained or custom trained model, you can deploy it with the watson-nlp-runtime container. This provides a stable API for the NLP capabilities described, regardless of the algorithm used to train the model. Please refer to my other blogs for more details of how to package and deploy models as containers: